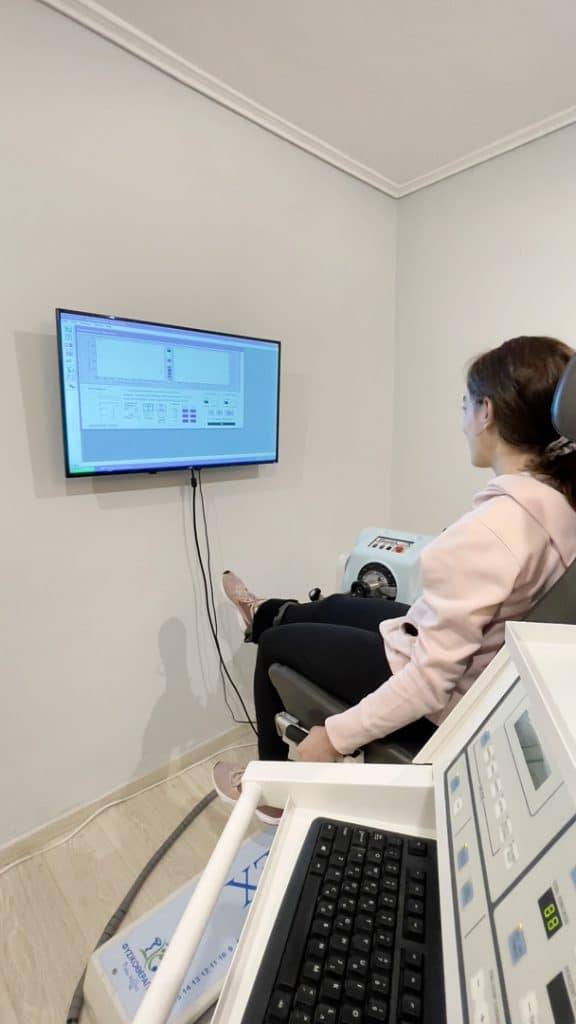
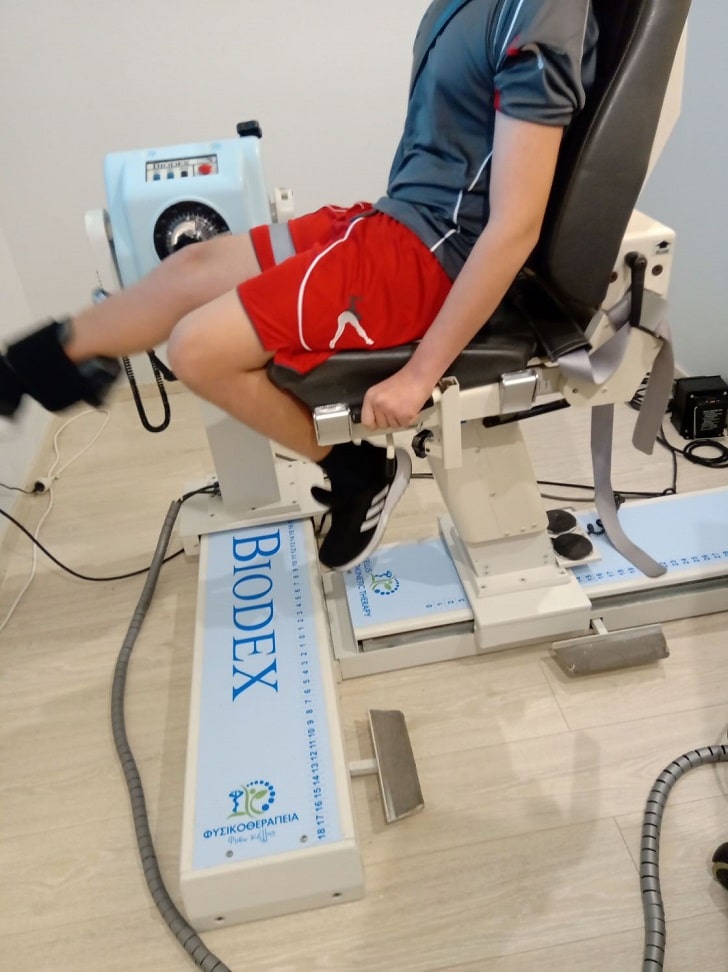
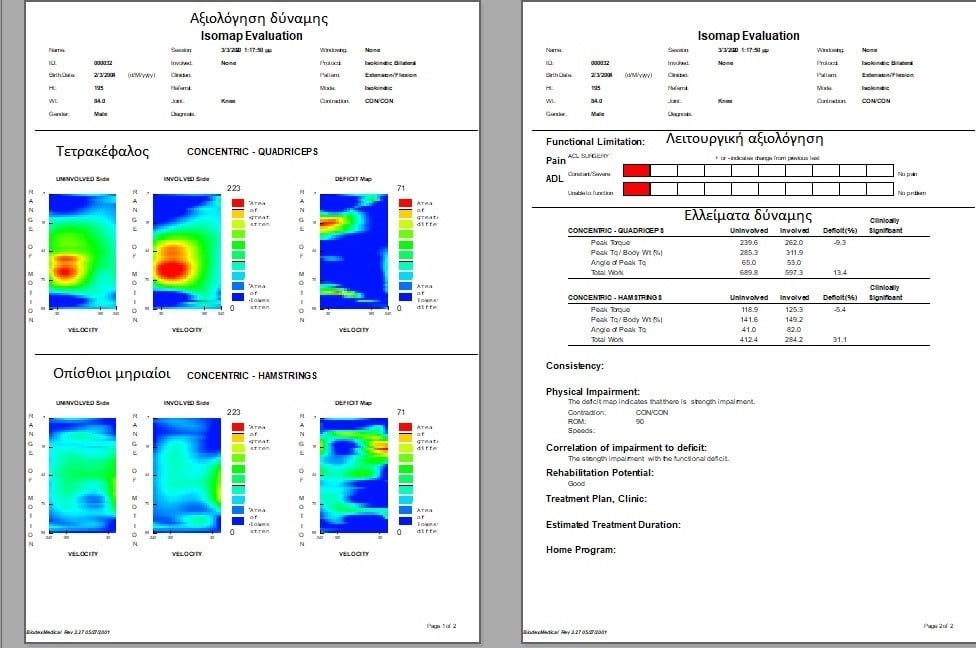
Θεραπεία ισοκινητικής δυναμομετρίας

ISOKINETIC TRAINING
What is it?

This represents one of the safest and valid methods of assessing and increase muscle strength:
Isokinetic exercise aims to:
1. Increase muscle strength
2. Improving the range of motion
3. Improving the function of the tendons
4. Improving coordination
How do we know that isokinetics are effective?
Scientific research 1,2 has shown that isokinetic exercise contributes significantly to the diagnosis and strengthening of muscles in conditions such as:
- Muscle injuries
- Sprains
- Anterior cruciate ligament rupture
- Epicondylitis
- Tendonitis and tendon diseases
- Osteoarthritis
- Atrophies of the trunk muscles
- Rupture of menisci
- Other ligament injuries
- Atrophies
How is it applied?
Isokinetics involvements performance of exercises at various testing velocities. Exercises in our clinic involve knee, hip and ankle joint movements.
How long does it take to see first results?
It depends of the aim of the program. For a typical strengthening conditioning program, first results can be seen within the 3-4 weeks when exercising 3 days a week . It is expected that after this period, there is a 10-15% increase in muscle mass, muscle strength imbalances are reduced to less than 10% and range of motion can increase up to 10%

Ask for our special therapy programs
ΒReferences
- Kellis E, Baltzopoulos V. Isokinetic eccentric exercise. Sports Medicine 1995; 19:202–222. Published online: March 1995.
- Kellis E, Galanis N, Kofotolis N. Hamstring-to-Quadriceps Ratio in Female Athletes with a Previous Hamstring Injury, Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction, and Controls. Sports 2019, Vol. 7, Page 214 2019; 7:214.